Definition:
The “All-Seeing Eye,” also known as the “Eye of Providence” or the “Eye of God,” is a symbol often depicted as an eye enclosed in a triangle and surrounded by rays of light or glory. However, it can also be any symbol of an eye in relation to God. It represents divine providence, where the eye symbolizes the omniscience and omnipresence of a higher power, often God, watching over humanity.
Etymology:
The term “All-Seeing Eye” comes from the idea of an eye that can see everything, indicating an entity that is all-knowing and ever-present. “Providence” refers to the protective care of a divine power.
Description:
The eye is often referred to as the “All-Seeing Eye.” Just as Santa Claus watches over children and judges whether they have been good enough to receive gifts, the religious are taught that God does the same. God is believed to be all-seeing and omnipresent; He sees everything you do and hears everything you say and think. And God is a judge; He will punish or reward you according to His own standards. For instance, according to many Christians’ interpretation of the Bible, He may send you to hell if He is compelled to watch you masturbate.
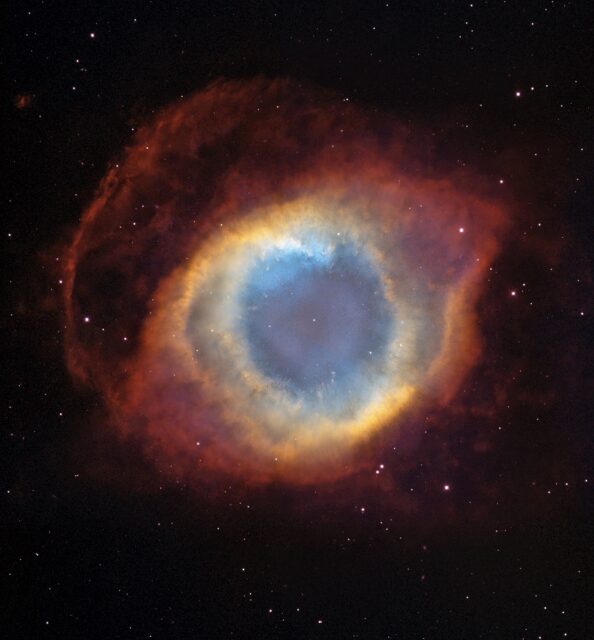
The “Helix Nebula” (NGC 7293) is a large planetary nebula located in the constellation Aquarius, about 650 light-years from Earth. It is one of the closest and most well-known examples of a planetary nebula, which is formed when a star similar to our Sun nears the end of its life and sheds its outer layers, leaving behind a glowing shell of gas and dust with a hot, dense core called a white dwarf at its center.
The Helix Nebula is often referred to as the “Eye of God” or “God’s Eye” due to its striking appearance in images taken by telescopes. When viewed from Earth, the nebula’s shape resembles a giant, colorful eye looking out into space. The nickname “God’s Eye” comes from its resemblance to a human eye, with the central white dwarf resembling the pupil, surrounded by rings of glowing gas that form the iris and sclera.
A cave in Iskar Gorge, Bulgaria named “Prohodna” is known for the two eye-like holes in its ceiling. The cave is known as “God’s Eyes.”

Symbolism:
An eye carries the symbolism of surveillance, represented by examples such as security cameras, monoculars, or an eye spying through any peephole.
The All-Seeing Eye monitoring the earth was chosen as the symbol for the Information Awareness Office, a former organization in the USA that operated under the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The organization aimed to develop technologies to enhance the government’s ability to monitor, collect, and analyze information about individuals.

The Office of Naval Intelligence (ONI) is a U.S. intelligence organization that is part of the United States Department of the Navy. The purpose of ONI is to collect, analyze, and disseminate intelligence information to support naval operations and decision-makers. ONI and several of its divisions have symbols that include an eye.
In the video game series “Halo,” ONI is a division of the United Nations Space Command (UNSC) responsible for intelligence gathering, espionage, and various clandestine operations. The emblem typically features an eye symbol, reflecting the organization’s focus on surveillance and intelligence. The design incorporates elements such as a bird or eagle, often symbolizing power and authority, along with other motifs that suggest secrecy and control.
In the USA, there is a program between the police and the local community called Community Road Watch, which is a community-driven traffic surveillance initiative aimed at reporting those who violate traffic rules. When driving on roads monitored by Community Road Watch, you will see signs for Road Watch.

In the USA, there is a program between the police and the local community called Neighborhood Crime Watch, which is a community-driven initiative for monitoring and reporting suspicious behavior. These signs are put up in neighborhoods that have implemented the program.
The Virtual Global Taskforce (VGT) is an international alliance of law enforcement organizations working together to combat child abuse on the internet and other online crimes against children. Established in 2003, the VGT aims to pool resources, expertise, and efforts from various countries to address the challenges related to children’s safety online.

London chose to announce the implementation of CCTV on buses by putting up posters at bus stops featuring simple eyes above a bus with the text: “Secure beneath the watchful eyes.”

In “The Lord of the Rings,” there is an eye at the top of a tower referred to as “The Eye of Sauron” or “The Eye of Mordor.” The Eye of Sauron is a powerful and malevolent force belonging to the character Sauron, a dark lord who rules over the region of Mordor. The eye is described as an all-seeing eye that symbolizes Sauron’s surveillance and control over the world.
In hospitals, there is a department called the Intensive Care Unit, which is an area dedicated to patients who require intensive monitoring. The abbreviation used for the Intensive Care Unit is ICU, which is pronounced “I see you” or “eye see you.”
The horror-thriller film “I.C.U.” (2009), which revolves around a group of teens who stumble upon a brutal murder while playing with surveillance cameras, uses one–eye symbolism to promote the movie.
The movie “Eagle Eye” (2008) revolves around two strangers, Jerry Shaw and Rachel Holloman, who are brought together by a mysterious phone call from a government supercomputer. This voice seems to have omnipresent control over their lives, manipulating all electrically connected systems, such as traffic lights, security systems, and telecommunications.

The science-fiction movie “Tau” (2018) revolves around a young woman named Julia, who is abducted by a scientist named Alex and forced to participate in his sinister experiment. Trapped in a futuristic smart house controlled by an advanced artificial intelligence called Tau, Julia must outsmart both the AI and her captor to secure her freedom. Tau is visually represented as a red robotic eye within a triangle, which is also featured on the movie poster. The poster also features the silhouette of a woman running or walking toward a glowing, circular red-orange robotic eye encased within a triangular structure. She looks over her shoulder, and while her face is not visible, the posture suggests that if her face were shown, only her left eye would be visible. Her left eye placed within the triangle is symbolically forming the Eye of Providence.

The poster for the thriller film “Eye in the Sky” (2015), which explores the ethical and moral dilemmas of modern drone warfare and counter-terrorism operations, incorporates the Eye of Providence to symbolize surveillance. The character Colonel Katherine Powell is shown in profile, with only her left eye visible. This eye is positioned within the triangular-shaped field-of-vision lines from the drone, forming a visual echo of the Eye of Providence within a triangle, also known as the Illuminati symbol.

The Eye of Providence is a prominent symbol on the reverse side of the Great Seal of the United States.

The Great Seal of the United States also appears on the back of the U.S. one-dollar bill and has been there since 1935.
The Eye of Providence can be found in various types of places of worship.
There’s an Eye of Providence above the altar in the Lucerne Church of St. Leodegar, Switzerland.

There’s an Eye of Providence on a piece altar equipment from the old Catholic cathedral in Pala, Kerala state, India. Now found in the nearby Thevarparampil Kunjachan Museum.

There’s an Eye of Providence at the altar in Arnøy Church in Arnøy, Norway.
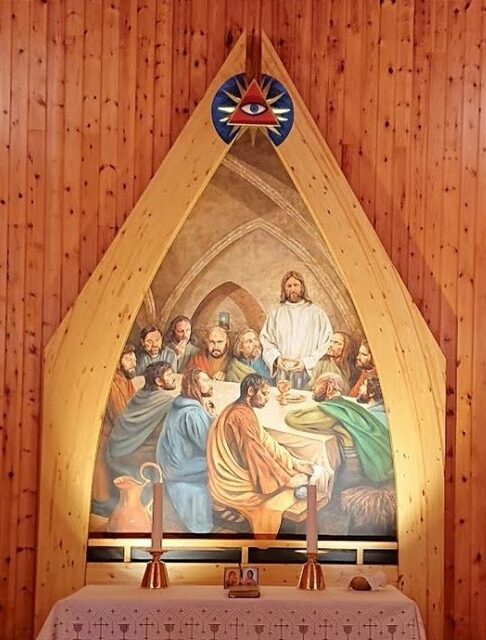

There’s the Eye of Providence on an altarpiece in Our Lady’s Church in Trondheim, Norway.
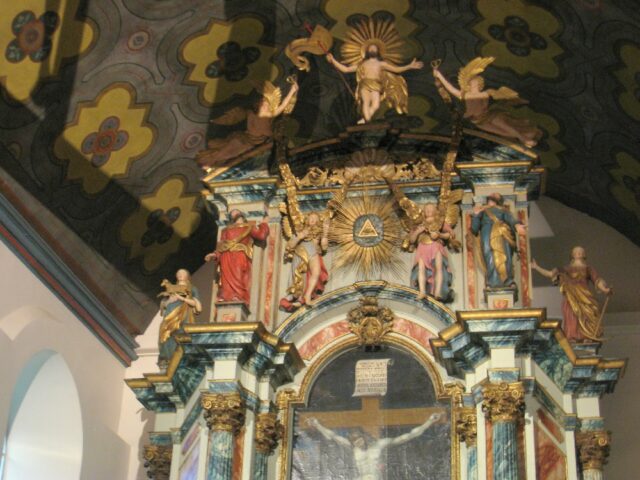

There’s an Eye of Providence in the dome ceiling in Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
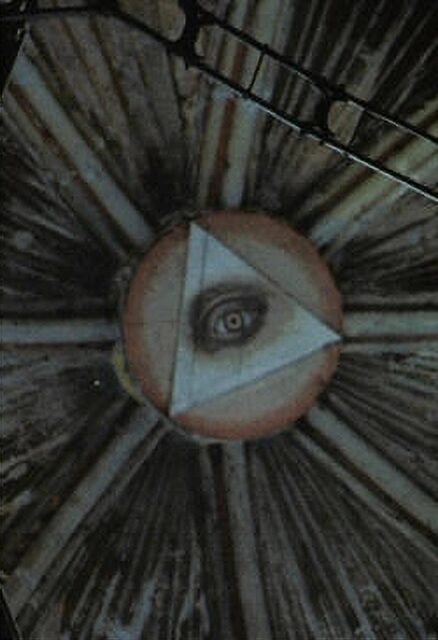

There’s an Eye of Providence in a ceiling painting in the Dormition of the Theotokos Cathedral in Romania.

There’s an Eye of Providence on the exterior of a cathedral in Salta, Argentina.
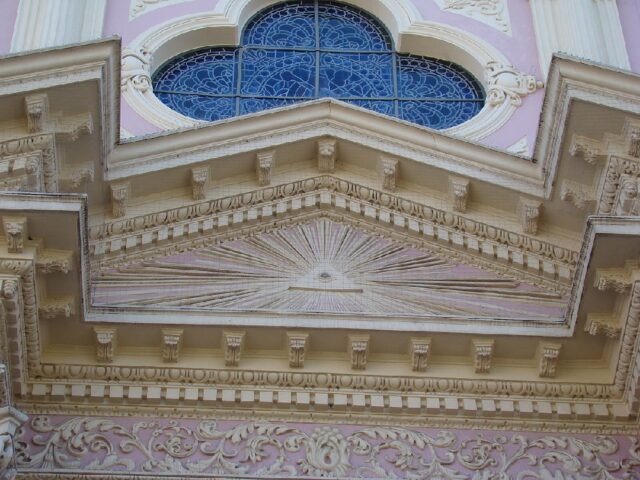

There’s an Eye of Providence on the exterior of the Masonic Temple of Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain.

There’s an Eye of Providence on the facade of the Gate of Dawn in Vilnius, Lithuania.
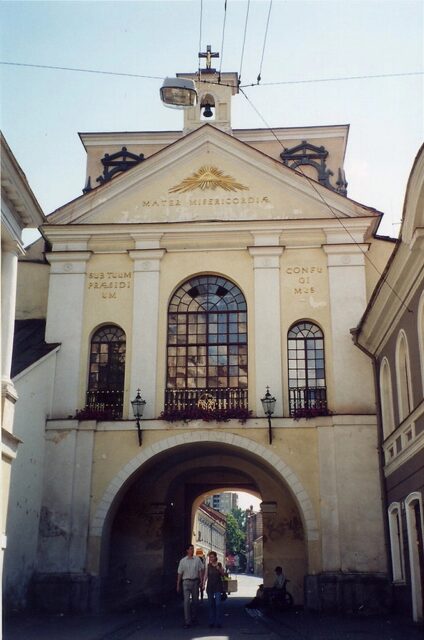

There’s an All-Seeing Eye in a pediment of an Esoteric Christian temple in Mount Ecclesia, California.
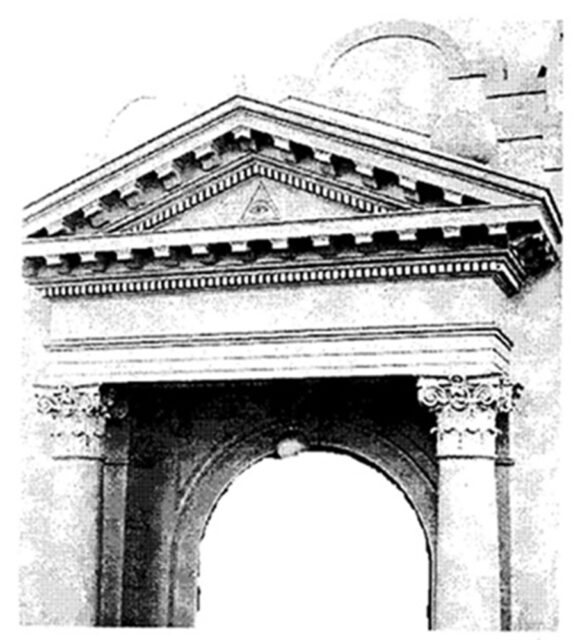

There’s an All-Seeing Eye on the gate of Aachen Cathedral in Germany.

The Eye of Providence in Church of the Annunciation in Nazareth, Palestine.
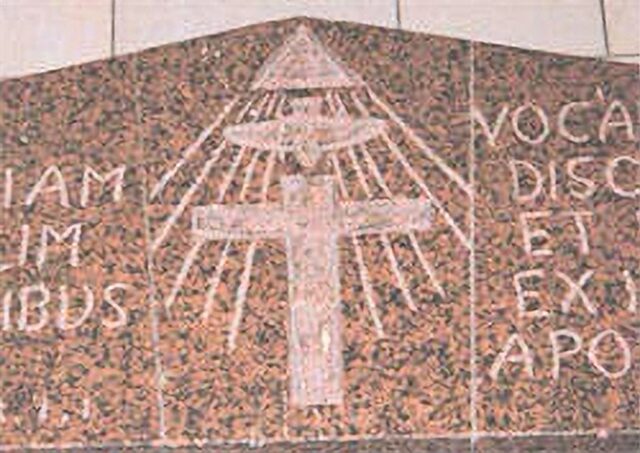

There was an Eye of Providence at the Church History Museum in Salt Lake City, which was built in the 1980s, but it has since been replaced.
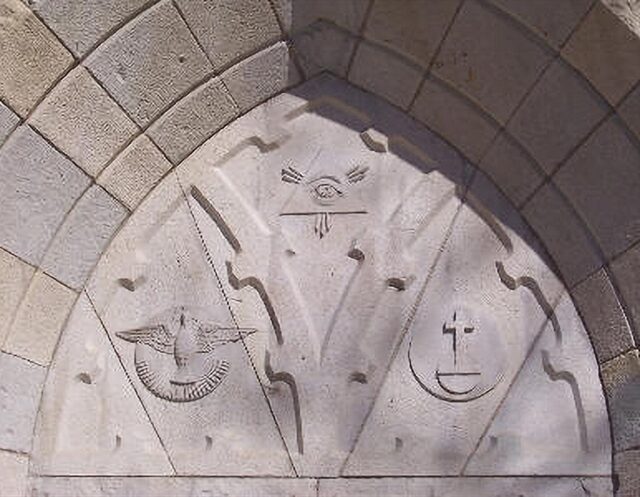

There’s the Eye of Providence on a Catholic church in Zamość, Poland.
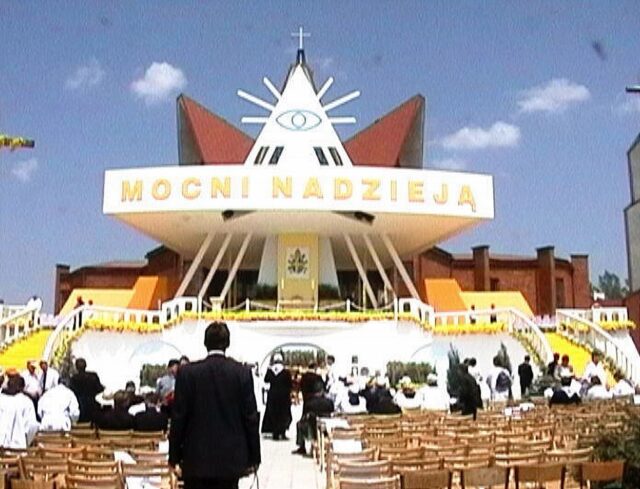

There’s an Eye of Providence in a mosaic window of George Washington in The White House Chapel in Washington, USA.

There’s the Eye of Providence depicted in a stained glass window in the St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Church in Fifield, Wisconsin.
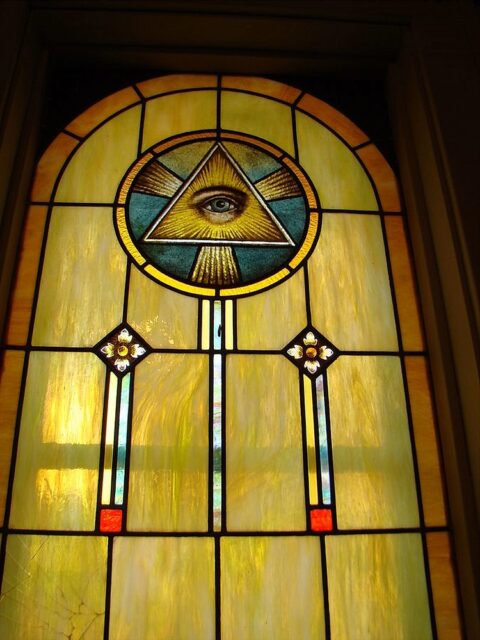

There’s the Eye of God on the apse chapel ceiling in the Cathedral Basilica of the Assumption, Lviv, Ukraine.

There’s the Eye of God on a drum at Odd Fellows Hall, Capitol Hill in Seattle, Washington.

There’s the Eye of Providence on a religious relief located in Rome’s Piazza del Popolo (People’s Square). This specific relief is part of the Santa Maria del Popolo church, which is situated in the square.

The lion in “The Chronicles of Narnia,” named Aslan, is widely interpreted as a representation of God or a Christ-like figure in Narnia.
Aslan is a central character in C.S. Lewis’s “Chronicles of Narnia” series, and he plays a similar role throughout the books and their film adaptations. Aslan embodies qualities such as wisdom, power, and compassion, and he acts as a guide, protector, and redeemer for the characters in Narnia.
In Narnia, Aslan is the ultimate authority and the creator of the world, which aligns with the concept of God in Christian theology. He is not just a powerful creature but the source of morality and goodness in the Narnian universe.
Aslan is often seen as an allegorical representation of Jesus Christ. In the earlier book and film, “The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe,” Aslan sacrifices himself for the sins of others and is resurrected, mirroring the story of Christ’s crucifixion and resurrection. His actions throughout the series reinforce this parallel.
The game cover of “God of War III” (2010) prominently features a close-up of Kratos’s eye. God of War III is the third main installment in the God of War series, continuing the story of Kratos as he embarks on a quest for revenge against the Olympian gods. In God of War III, the eye of Kratos can be seen as a representation of his ability to see through the lies and manipulations of the gods.

The music album cover for “The Cranberries: Bury the Hatchet” (1999) features a naked human in the desert, crouching in discomfort under the stalking and surveillance of a hovering Eye of God.
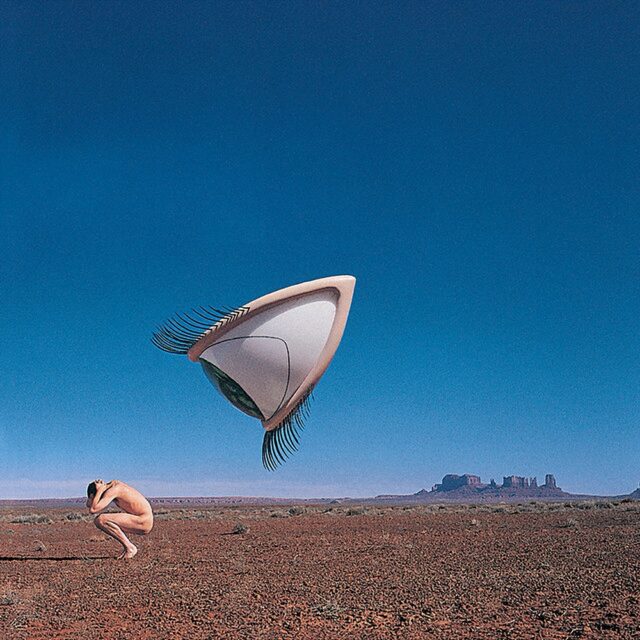

The cover of “Eye in the Sky,” a 1957 science fiction novel by Philip K. Dick that revolves around a group of people who, after a near-death experience in a particle accelerator accident, find themselves trapped in alternate realities based on their subconscious perceptions and beliefs, features a large eye watching over a group of people who seem to be running from it across a surreal, otherworldly landscape.

The EP cover for “Misfits: Ghouls Gold E.P.” (1988) features the image from the Philip K. Dick novel “Eye in the Sky.” A skull has been added to the pupil of the eye. The eye appears to be watching or stalking the characters below, creating a sense of paranoia or being pursued. In the foreground, there are several people running in what looks like a panicked escape. The greenish tint of the cover adds to the eerie and otherworldly atmosphere, which is often associated with ghostly or supernatural themes.

The most prominent feature of the music album cover for “Mute: Thunderblast” (2013) is the large eye positioned in the center of a dark, ominous cloud. A powerful lightning bolt strikes downward from the cloud, directly at a small, silhouetted human figure below. The lightning bolt is often associated with divine wrath or judgment, reminiscent of ancient depictions of gods like Zeus or Thor, who wield lightning as a weapon. The imagery here suggests that the eye is not only watching but actively intervening, possibly punishing or overpowering the figure below.

The music album cover for “Rihanna: Unapologetic” (2012) features a topless Rihanna with various handwritten words overlaying her image. The word “Love” is written in front of her left eye. As only eye is visible beside the eside the word “Love,” it emphasizes that love is fantasy. The handwriting makes it difficult to discern whether it says “Love,” or “Joe.” Joe is God in the Bible, and one eye is a symbol for God. As only one eye is visible beside the name “Joe,” it emphasizes that God is fantasy. The Bible explicitly states that “God is love.” As it says in 1 John 4:8 (NIV), “Whoever does not love does not know God, because God is love.” And in 1 John 4:16 (NIV), it states, “And so we know and rely on the love God has for us. God is love. Whoever lives in love lives in God, and God in them.” Since God does not exist and is a lie, this emphasizes that love is a fantasy.

The movie poster for “The Imaginarium of Doctor Parnassus” (2009) features a lot of Masonic symbolism.
There’s a floor with a chess-tiled pattern, resembling a checkerboard. A chessboard is a battlefield for strategic moves and counter-moves, which can symbolize the various manipulations and decisions that characters in the film must make. The presence of this pattern suggests that the characters are like chess pieces in a larger game controlled by higher forces, such as Doctor Parnassus and Mr. Nick (the Devil).
In the center of the movie poster is a golden, ornate archway, which symbolizes the entrance to the “Imaginarium,” a magical realm where the characters’ imaginations come to life. The archway leads into a vivid, dreamlike landscape filled with bizarre and fantastical imagery, reinforcing the film’s themes of escapism, fantasy, and the battle between good and evil.
The All-Seeing Eye is subtly placed near the top center of the poster, nestled among the elaborate designs. The presence of this symbol could be interpreted as a reference to the themes of fate, destiny, and the idea of a higher power observing and influencing the events within the story. In the film, Doctor Parnassus is a character who has made deals with the devil and possesses mystical powers, so the Eye of Providence might also symbolize the overarching forces of morality, judgment, and the consequences of one‘s actions.

The logo for the franchise “National Treasure” features the Eye of Providence as part of the Illuminati Symbol.
The National Treasure movies revolve around uncovering secrets related to American history and the founding of the United States. The Eye of Providence is deeply connected to American iconography and Freemasonry, both of which play significant roles in the plot. The symbol is associated with the Founding Fathers and is a recurring motif in the mysteries that the characters unravel.
The inclusion of the Eye of Providence in the logo underscores the film’s themes of conspiracy theories, secret societies, and the pursuit of hidden treasures. The eye suggests that there is more beneath the surface, inviting viewers into a world where ancient symbols hold the key to unlocking historical secrets.

The most striking element of the album cover for “Nightwish: Oceanborn” (1998) is the large, serpent-like eye that dominates the upper part of the image. Within the eye’s pupil, the Earth is depicted, which may suggest that the eye is observing the world, much like the Eye of Providence is often interpreted as the all-seeing eye of God. This imagery conveys a sense of cosmic awareness or omniscience.

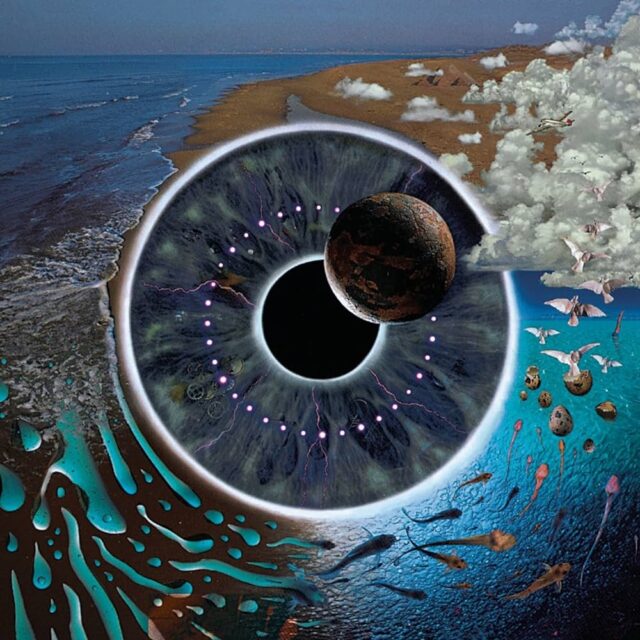
The cover of the live music album “Pink Floyd: Pulse” (1995) features a massive, detailed eye. This eye is highly stylized, with the iris and pupil taking on cosmic and aquatic qualities. Within the eye, you can see planet Earth, symbolizing the eye observing our world. Surrounding the eye are elements from Earth, such as waves, clouds, and what appear to be natural forms of life like birds and fish. The eye on the cover can be interpreted as a representation of the “Eye of God” or the “Eye of Providence,” although it is more abstract and artistic in this context. It symbolizes a window into multiple layers of existence—cosmic, earthly, and aquatic realms—suggesting that the eye is a gateway to understanding or perceiving the universe’s interconnectedness.

The music album cover for “Death: Symbolic” (1995) is striking and symbolic, with a strong visual focus on an eye, which can be interpreted as the Eye of God or Eye of Providence in a more abstract and surreal context. The eye is surrounded by abstract, dark, and chaotic elements, giving it an ominous and almost supernatural presence. The eye appears to be observing the scene below, suggesting a watchful, all-seeing entity that is observing everything happening in this surreal environment.

The music album cover for “Dream Theater: Train of Thought” (2003) features a large, solitary eye positioned on the forest floor, seemingly embedded in the ground. The eye is realistically rendered, creating a sense of unease and mystery as it stares out from the landscape. The eye‘s placement and the way it emerges from the earth suggest that it is a powerful, watchful presence within this otherwise quiet and eerie forest.

The broadway musical “The Book of Mormon” is a story that follows two young missionaries sent to Uganda in an attempt to convert the local population to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. They quickly realize that the idyllic vision of missionary work they had been expecting does not align with the harsh realities faced by the villagers, who live in extreme poverty and fear due to warlords, disease, and famine. “Hasa Diga Eebowai” is a song performed by the villagers as they explain to the missionaries how they cope with their dire circumstances. The phrase “Hasa Diga Eebowai” is presented as a traditional saying that helps the villagers deal with their suffering. The villagers explain that “Hasa Diga Eebowai” translates to “Fuck you, God” in their language, a phrase that expresses their anger and frustration with the hardships they endure.
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a.
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a.
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a.
Fuck you in the eye!
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a (Hasa Diga Eebowai!).
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a.
Fuck you, God, in the ass, mouth, and cunt-a (Hasa Diga Eebowai!).
Fuck you in the other eye!
In “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald, the eyes of Dr. T.J. Eckleburg play a significant symbolic role in the novel. These eyes are depicted on a faded billboard that overlooks the desolate area known as the “Valley of Ashes,” a barren, industrial wasteland between West Egg and New York City.
The billboard features a pair of enormous, disembodied blue eyes behind large yellow spectacles. The eyes are all that remains of an old advertisement for an oculist named Dr. T.J. Eckleburg. The billboard is described as being weathered and faded, giving the eyes an eerie, ghostly appearance.
One of the most famous interpretations of the eyes is that they symbolize the eyes of God, watching over the characters’ immoral behavior and the corruption that permeates the novel. This is particularly emphasized in a scene where George Wilson, a key character, remarks that the eyes of Dr. T.J. Eckleburg are like the eyes of God, seeing everything. Wilson is deeply religious and, in his grief and confusion, he interprets the billboard as a sign of divine judgement.

Articles:
Eye
Definition: The “eye” is a complex sensory organ responsible for vision. It detects light and converts it into electrochemical signals, which are then processed by the brain to produce images….
Eye of Deception
Definition: The “Eye of Deception” is a symbolic representation that what is being observed or conveyed is false or misleading. It serves as a warning or indication that what is…
Eye of Fantasy
Definition: “Eye of Fantasy” refers to the symbol of a single eye used to represent a situation that is impossible, unrealistic, or inaccurate. It is often used to indicate that…
Eye of Jesus
Definition: The term “Eye of Jesus,” also known as the “Eye on the Cross,” typically refers to a metaphorical or symbolic concept within Christian theology and spirituality. It is not…
Eye of the Devil
Definition: The “Eye of the Devil” typically refers to a malevolent, watchful gaze that symbolizes evil, misfortune, or a sinister presence. It can be interpreted literally, as an actual eye…
Eye of Truth
Definition: The “Eye of Truth” is a symbolic concept carrying dual meanings. The Eye of Truth is used by spiritual people as a metaphor for seeing that which does not…
Eyes of Horus
Definition: The “Eyes of Horus” is an ancient symbol originating from ancient Egyptian mythology where a set of two eyes were referred to as the Eyes of Horus, Udjat, or…
Illuminati
Definition: “Illuminati” refers to individuals who understand how language, religion, and the world system are scams. Etymology: The term “Illuminati” originates from Latin and means “the enlightened.” It is derived…
The Great Seal of the United States of America
Definition: The Great Seal of the United States is a national seal that symbolizes the authority and sovereignty of the federal government. Description: The Great Seal was adopted by the…
Tower of Babel
Pieter Bruegel the Elder: The Tower of Babel (1563). Lucas van Valckenborch: Tower of Babel (1594). Gustave Doré: The Confusion of Tongues. Definition: “Babel’s Tower” is a fictional tower from…
Religion:
While the specific image of the All-Seeing Eye is not directly mentioned in religious texts, the concept of an omniscient and omnipresent deity is prevalent:
- In the Bible, in Proverbs, chapter 15, verse 3 (NIV), it says: “The eyes of the Lord are everywhere, keeping watch on the wicked and the good.”
- In the Bible, in Psalm, chapter 33, verse 18 (NIV), it says: “But the eyes of the Lord are on those who fear him, on those whose hope is in his unfailing love.”
- In the Quran, in Surah Al-Baqarah 2:115 (Sahih International), it says: “And to Allah belongs the east and the west. So wherever you [might] turn, there is the Face of Allah. Indeed, Allah is all-Encompassing and Knowing.”
- In the Bhagavad Gita, in chapter 13, verse 27, it says: “The Supreme Lord is situated in everyone’s heart, O Arjuna.”
One eye is a common symbol for a god, as gods are fictional characters, literally meaning “fantasy.” Religions throughout history have featured multiple gods and goddesses symbolized by an eye, such as:
- In Japanese mythology where Izanagi created the sun goddess Amaterasu from his left eye and the moon god Tsukuyomi from his right eye.
- In Egyptian mythology, several gods has been depicted with one eye, such as Horus, Ra, Osiris, Thoth, Sekhmet, Bastet, Isis, Ptah, Atum, and others. The ancient Egyptian way of drawing, called the Egyptian canon or Egyptian artistic convention, consistently poses characters so that they are always shown with only one eye visible.
- In Celtic mythology, Balor was a god who had an evil eye capable of killing anything it looked at. Cailleach, a Scottish goddess of winter and natural forces, was often depicted with a blind eye that she could open and close to control the weather.
- In Haitian Voodoo, Baron Samedi is a god who is sometimes depicted with only one eye.
- In Norse mythology, Hel is a goddess who rules over death and the underworld, and in pop culture, she is often depicted with only one eye. Odin, on the other hand, sacrificed one of his eyes at Mimir’s well in exchange for wisdom and insight.
- In Hinduism, Shiva is often depicted with a third eye, also known as Nazar Boncugu. Ganesha, one of the most worshipped deities in Hinduism, is known as the “Lord of Obstacles” or the “Remover of Obstacles.” He is one of the most recognizable deities due to his distinctive appearance with an elephant’s head and a human body, and he is also most often depicted with a third eye.