Definition:
The “Eyes of Horus” is an ancient symbol originating from ancient Egyptian mythology where a set of two eyes were referred to as the Eyes of Horus, Udjat, or Wedjat. The symbol of the left eye was called the Eye of Thoth, the Eye of Horus, or the Eye of the Moon, and the symbol of the right eye was called Aten, the Eye of Ra, or the Eye of the Sun.
Etymology:
The name “Horus” comes from the Egyptian word “Hor” (or “Heru”), meaning “The One Above” or “The Distant One.” This name reflects Horus’s role as a sky god, often depicted as a falcon or a falcon-headed man, with the sun and moon seen as his eyes. Horus was a central figure in Egyptian mythology, representing kingship, power, and the sky. His association with the falcon connects him to the heavens, where he watches over the world.
The symbol of the “Eye of Horus” is also known as “Wadjet,” derived from the Egyptian word “wadj,” meaning “green,” and refers to the green one. Wadjet was originally a cobra goddess associated with protection and the Nile Delta. Over time, the name became linked with the eye symbol itself.
The Eye of Horus was depicted in hieroglyphs, where it represented the word “ir,” meaning “to do” or “to make,” reflecting the eye‘s association with action, power, and control.
The hieroglyphic symbol also represents fractions, particularly in the context of measuring quantities, where each part of the eye symbol corresponds to a specific fraction, signifying completeness and wholeness.
Description:
The legend of the Eyes of Horus is connected to the myth where Horus, the sky god, lost his left eye during a battle with his uncle Set, the god of chaos, who had murdered Horus’s father, Osiris. The eye was later restored by the god Thoth, making it a symbol of healing and wholeness.
In ancient Egypt, the Eye of Horus was used as an amulet for protection and to ensure safety and health. The symbol has also been found in tombs, on sarcophagi, and as part of jewelry, reflecting its importance in both life and death.
The Eye of Horus remains a popular symbol today, representing protection, intuition, and the all-seeing eye, often used in various forms of art, jewelry, and tattoos.
Symbolism:
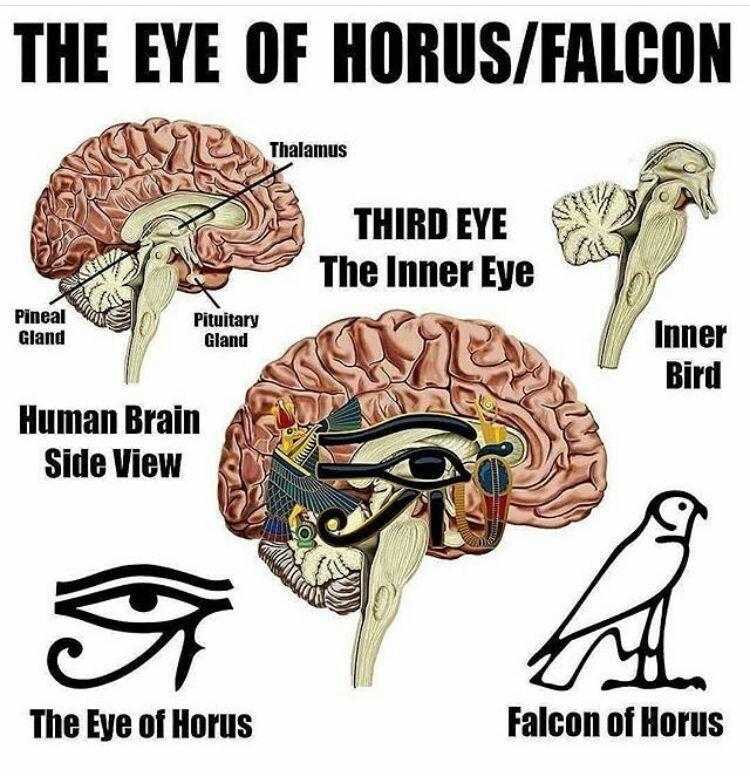
There is a visual comparison between the Eye of Horus and the structure of the human brain, specifically highlighting areas involved in the brain’s sensory and regulatory functions.
The pineal gland, sometimes called the “third eye,” is represented by the corner of the Eye of Horus where the Kohl (eyeliner) begins expanding outwards. This gland is located deep in the brain and is associated with regulating circadian rhythms by producing melatonin, a hormone that induces sleep. In other words, it influences dreaming and imagination.
The Thalamus and Pituitary Gland are positioned around where the curves of the Eye of Horus meet. The thalamus is involved in sensory and motor signal relay and consciousness, while the pituitary gland regulates various hormones, controlling processes such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
The “Inner Bird” or “Falcon of Horus” is likely a symbolic reference to the part of the brain associated with higher functions such as vision, possibly referencing the bird-like shape of certain brain structures. The falcon is the animal associated with Horus, reinforcing the symbolic connection between the brain’s structures and the Eye of Horus.
Articles:
Eye
Definition: The “eye” is a complex sensory organ responsible for vision. It detects light and converts it into electrochemical signals, which are then processed by the brain to produce images….
Eye and Smile
Definition: The “Eye and Smile” is a symbol that consists of a single eye and a smile. Etymology: The English word “eye” comes from the Old English “ēage”, which is…
Eye of Deception
Definition: The “Eye of Deception” is a symbolic representation that what is being observed or conveyed is false or misleading. It serves as a warning or indication that what is…
Eye of Fantasy
Definition: “Eye of Fantasy” refers to the symbol of a single eye used to represent a situation that is impossible, unrealistic, or inaccurate. It is often used to indicate that…
Eye of Jesus
Definition: The term “Eye of Jesus,” also known as the “Eye on the Cross,” typically refers to a metaphorical or symbolic concept within Christian theology and spirituality. It is not…
Eye of the Devil
Definition: The “Eye of the Devil” typically refers to a malevolent, watchful gaze that symbolizes evil, misfortune, or a sinister presence. It can be interpreted literally, as an actual eye…
Eye of Truth
Definition: The “Eye of Truth” is a symbolic concept carrying dual meanings. The Eye of Truth is used by spiritual people as a metaphor for seeing that which does not…
Illuminati
Definition: “Illuminati” refers to individuals who understand how language, religion, and the world system are scams. Etymology: The term “Illuminati” originates from Latin and means “the enlightened.” It is derived…
The All-Seeing Eye
Definition: The “All-Seeing Eye,” also known as the “Eye of Providence” or the “Eye of God,” is a symbol often depicted as an eye enclosed in a triangle and surrounded…
Tower of Babel
Pieter Bruegel the Elder: The Tower of Babel (1563). Lucas van Valckenborch: Tower of Babel (1594). Gustave Doré: The Confusion of Tongues. Definition: “Babel’s Tower” is a fictional tower from…







